The limit of a straight skeleton is the distance at which the inner offset disappears completely. You can get the geometry left at the limit as a polyline set consisting of isolated vertices and/or segments.
Value
skeleton_limit returns a euclid_exact_numeric vector and
skeleton_limit_location returns a polyclid_polyline_set vector
See also
Other straight skeleton functions:
skeleton_interior(),
skeleton_offset()
Examples
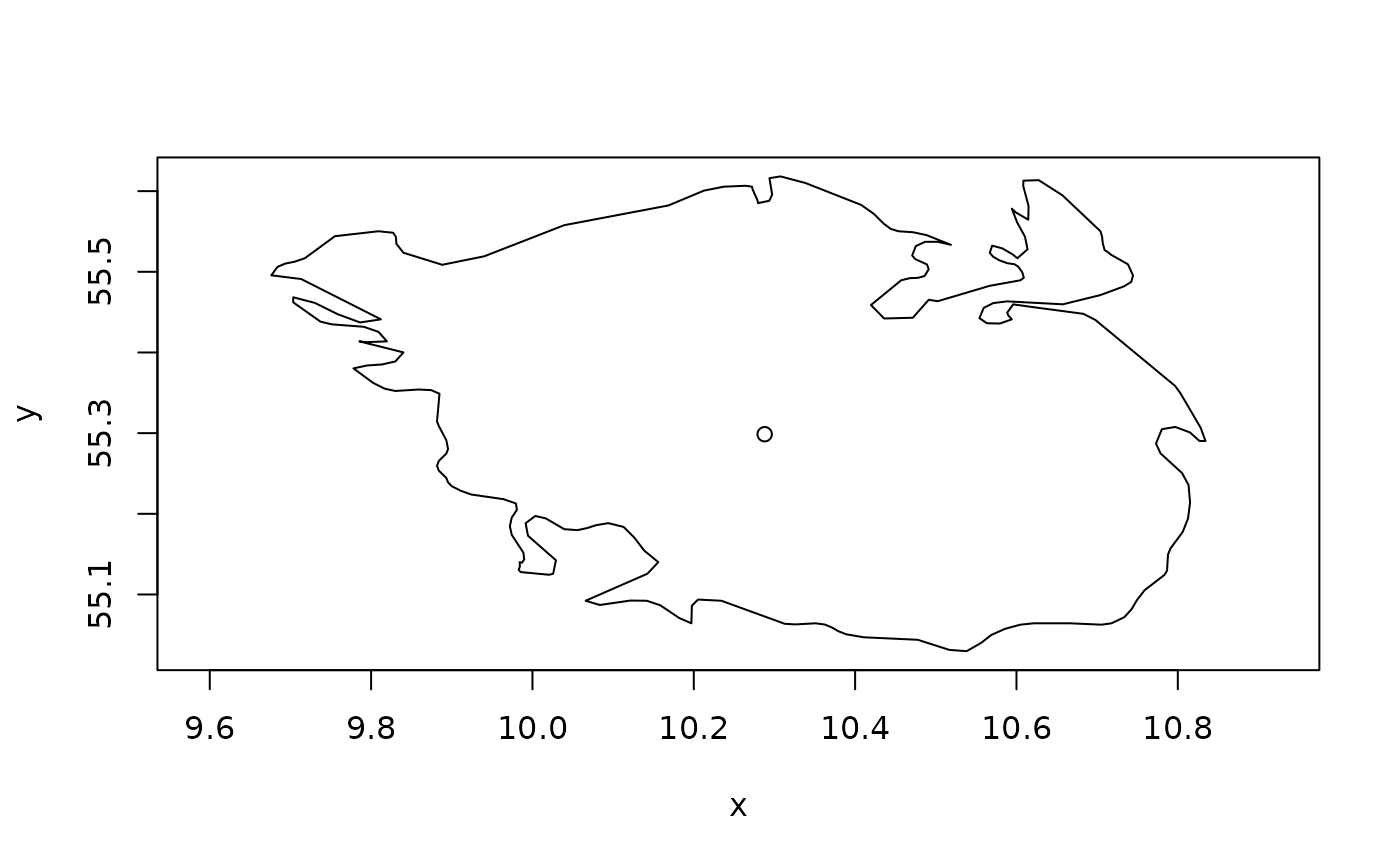
poly <- polyclid::denmark()[9]
# Complex polygons will often have a single limit point
plot(poly)
euclid_plot(vert(skeleton_limit_location(poly)))
# But certain geometries will result in segments rather than lines
poly <- polyclid::polygon(
c(1, 1, 2, 2, -2, -2, -1, -1),
c(-2, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, -2)
)
euclid_plot(skeleton_limit_location(poly))
 # You can get the distance from the limit location to the boundary
skeleton_limit(poly)
#> <exact numerics [1]>
#> [1] 1
# You can get the distance from the limit location to the boundary
skeleton_limit(poly)
#> <exact numerics [1]>
#> [1] 1